K2VIEW EBOOK
What is iPaaS Cloud Data Integration?
integration Platform as a Service Guide
iPaaS coud data integration standardizes the integration of applications and data,
allowing for the automation of business processes and the sharing of data across applications.

INTRO
Simplify Data Integration
According to analyst Gartner, iPaaS cloud data integration, or enterprise iPaaS, is foundational for supporting data integration and increasingly used for B2B integration and API management.
This guide covers cloud data integration definitions, challenges, purposes, benefits, use cases, capabilities, enterprise requirements, and a comparison with traditional Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) architectures. It concludes by highlighting a novel “Data Product Platform as a Service” approach.
CHAPTER 01
What is iPaaS Cloud Data Integration?
A cloud data integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) standardizes how applications and data are integrated in an organization, making it easier to automate business processes, and share data across applications.
It's a single platform that enables data teams to implement data, application, API and process integration projects, involving any combination of cloud-resident and on-premise endpoints. This is accomplished by developing, deploying, executing, managing, and monitoring integration processes/flows that connect multiple endpoints, in order to work together.
Typical iPaaS cloud data integration scenarios:
- Application-to-application (A2A) integration
- Business-to-business (B2B) integration
- Cloud service integration (CSI)
- Internet of Things (IoT) integration
- Mobile application integration (MAI)
Gartner considers a cloud data integration Platform as a Service to be "Enterprise" (EiPaaS) if it supports projects requiring high availability/disaster recovery (HA/DR), security, service-level agreements (SLAs), and technical support from the service provider.
CHAPTER 02
iPaaS Cloud Data Integration Challenges
Enterprises are constantly churning out applications, many of which are chosen by business units seeking “best of breed” and deployed as silos – but still need to be integrated with other apps, and share data across the organization. And business-critical processes – such as quote-to-cash, order fulfillment, item management, procure-to-pay, and more – span a variety of applications across multiple departments. Not to mention the growing volume of data from all data types and formats, flowing between applications.
Traditionally, enterprises integrated their business processes via a combination of custom programming, middleware, and/or enterprise application integration (EAI) implementations, like service-oriented architecture (SOA). But while such solutions worked fine, they typically took a lot of time to create and were expensive to run. They also left enterprises reliant on specific data silos, meaning that data couldn’t be shared among different consumers.
CHAPTER 03
Why iPaaS Cloud Data Integration?
iPaaS cloud data integration tools standardize how new applications are added and existing applications are integrated to an enterprise, making it easier to move all types of data across applications, while providing the necessary integration functionality as well.
Integration is standardized in the sense that iPaaS cloud data integration solutions dynamically monitor, maintain, and update processes across applications, which are constantly being added, deleted, or changed. When done right, iPaaS cloud data integration enables both data consumers and technical engineers the ability to easily build, manage, and maintain integrations.
CHAPTER 04
iPaaS Cloud Data Integration Benefits
In comparison with traditional integration solutions (e.g., out-of-the-box, point-to-point etc.), iPaaS cloud data integration benefits stand out, with:
- Quicker, easier integrations
With cloud data integration (iPaaS), there’s no need for lengthy planning processes, or large project teams. - Faster time to value
The service is available to both operations and development teams. All they need to do is subscribe and start integrating. - Better results, with less work, and no specialized skills
The platform achieves more improved and enriched integrations in shorter periods of time, and without the need for new integration functionality for each new addition. - Enhanced scalability
With the use of public cloud-based integration, business can grow to meet demands without having to worry about setting up yet another custom in-house integration. - Expanded use
Anyone in the organization can get the data they need, when they need it, when data and processes are updated across applications. - Lower integration costs
With cloud data integration (iPaaS), there’s no need for high-paid developers to generate code for custom integrations. Additionally, the SaaS model allows for monthly or yearly subscriptions, making it extremely cost-effective over time. And the service vendor is responsible for maintenance and storage of interconnected data. - Optimized B2B integration
Every enterprise has its own process for exchanging information with partners, but different applications, used at different companies, make it hard to communicate. - Embedded API management
With a cloud data integration platform, there’s no need to publish customer APIs, or combine APIs from other services. The platform is a more scalable and secure solution for managing APIs.
CHAPTER 05
Cloud Data Integration (iPaaS) Overview
iPaaS Cloud data integration is a single integrated platform that delivers a consistent process for data integration between all relevant apps in an enterprise, whether on premise or in the cloud.
The platform is hosted and managed on the cloud, and provided as a service. Subscribers need to choose the applications and services they need to integrate, and orchestrate the data flows between them. Everything else is the responsibility of the cloud provider, including data governance, feature updates, hardware management, security, and software fixes when necessary.
Pricing for the service typically comes in the form of a monthly subscription fee or a pay-as-you-go model.
iPaaS cloud data integration providers usually offer a wide range of integration scenarios, especially targeting highly regulated enterprises. The service allows for real-time data exchange between SaaS apps, as well as between SaaS apps and other cloud-based applications, SaaS, and on-premise applications.
CHAPTER 06
iPaaS Cloud Data Integration Use Cases
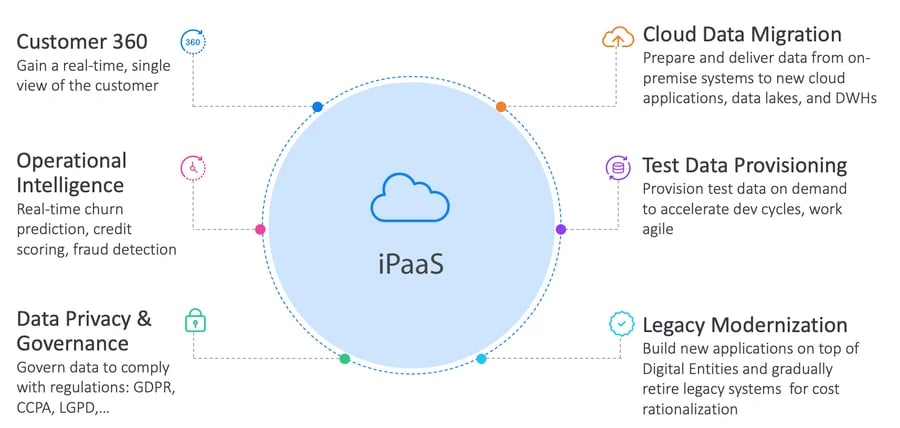
A growing number of enterprises count on iPaaS to manage applications and data more easily, integrate legacy systems more quickly, and resolve integration issues more thoroughly.
The top use cases of iPaaS cloud data integration include:
- Customer 360, for a trusted, holistic perspective of customer data, in real time.
- Data masking, that protects data at rest, in use, and in transit
- Test data management, that provisions high-quality test data, in minutes, on demand.
- Data migration, that moves data and digital business operations into the cloud.
- Legacy application modernization, that systematically moves legacy application functionality and data from old to new environments.
iPaaS cloud data integration enables highly-regulated industries – like telco and media, financial services, and healthcare – integrate data and systems quickly, securely, and in complete compliance, by using data making tools as necessary.
CHAPTER 07
iPaaS Cloud Data Integration Core Capabilities
Here are the core capabilities of a cloud data integration platform:
- Data connectivity
Data connectivity ingests data from any source, in any delivery mode, and then transforms it for delivery, to any target, in any format. - Data and application integration
Data integration creates and manages scalable data pipelines between source and target systems, for operational and analytical use cases. - Data orchestration
Data orchestration unifies, transforms, and enriches data, from any source systems into any target applications, quickly and easily. - Data governance
Data governance ensures data quality, enforces data privacy and security controls, and makes the data easily accessible at enterprise scale. - Data catalogue and data lineage
A data catalog is built into the company's data fabric to inventory and classify data assets, and visually map information supply chains to show data lineage.
Beyond the above, the platform must be able to handle lifecycle management and monitoring (management of the cloud integrations), error handling, and API management.
In short, the right cloud data integration solution should be flexible and scalable enough to meet the extremely demanding requirements of modern data management.
CHAPTER 08
Enterprise iPaaS Requirements
Enterprise iPaaS requires whole a new approach, coined “EiPaaS” by Gartner. EiPaaS needs to simplify the creation of complex integrations, and to shift integration management from IT to the data consumers, by providing clear-cut guidelines.
EiPaaS solutions need to address the following requirements:
- Security and protection
The enterprise solution should provide fundamental security like fraud detection, and user authorization. - Privacy compliance
iPaaS should ensure compliance with industry standards, like those issued by the Payment Card Security Standards Council, and privacy regulations, like GDPR. - Continuous delivery
Data teams should be able to design, integrate, and deliver applications, across the enterprise, whether the apps are developed internally, or on the cloud. - Continuous testing
The enterprise platform should also provide for testing, deployment, and automation – to enable faster time to market across all environments. - Support for leading cloud platforms
The right iPaaS tool integrate easily with leading cloud platforms – like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – as well as with locally hosted virtual architectures.
CHAPTER 09
ESB vs iPaaS
An enterprise service bus (ESB) is a layer of middleware that manages and shares, data and application components, across the organization. Although housed on premise, ESB systems can facilitate cloud integrations, and mimic hybrid cloud environments.
iPaaS takes over where ESB leaves off, especially in terms of enterprise-critical capabilities, as reviewed in the following table:
| ESB | iPaaS | |
|---|---|---|
| Remote hosting | No. ESB resides on-premise, and acts as a middle layer, between local data and services, and the cloud. | Yes. iPaaS is based in the cloud, or in a hybrid environment, where management tools are hosted remotely. |
| Multi-tenancy | No. ESB can’t host multiple users from single software instances. | Yes. Because, iPaaS is cloud-based, hosting multiple users in built in. |
| SaaS operations | No. Although ESB is ‘cloud-capable’, it isn’t a true cloud integration platform. | Yes. iPaaS operates in SaaS environments by definition. |
| Custom coding | No. Traditional ESB doesn’t respond as capably to changes in remote services as cloud-based services. | Yes. iPaaS is a hosted service that applies updates, security fixes, and other refinements, automatically. |
| Real-time response | No. ESB response times lag behind its iPaaS counterpart. | Yes. iPaaS responds in milliseconds, enabling proactive business intelligence. |
For enterprises that need to be flexible about future scaling, or adopting a new data integration architecture, iPaaS is clearly the better choice.
CHAPTER 10
Data Product Platform as a Service
A latest approach to EiPaaS is based on a data products.
Data Product Platform is the only iPaaS platform deployed in a public cloud (as well as offering an on-premise, and hybrid deployment options).
An enterprise cloud data integration (iPaaS) platform is highly effective because it delivers:
- Patented entity-based technology
When data is organized by business entity, and managed by Micro-Database™ (for example, one Micro-Database for every customer instance), performance is unparalleled. - Multi-use data schemas
An enterprise can build the data schema once, and use it for many different use cases, such as customer 360, data pipelining, test data management, and more. - Modular, open, and scalable architecture
Data integration, transformation, enrichment, preparation, and delivery are aggregated in a single, extensible platform. - Split-second, end-to-end, response times
Enterprise data fabric is built to support high-scale, high-volume operations in real time, with bi-directional data movement between sources and targets. - Data management for operational and analytical workloads
Integrated, trusted data is delivered in a split second into consuming applications, or pipelined into data lakes and data warehouses for analytical purposes.
CHAPTER 11
iPaaS Cloud Data Integration Vendors
There are multiple vendors offering enterprise-grade app/data integration tools solutions. The following table lists the pros and cons of the industry’s leading iPaaS cloud data integration vendors:
|
Vendors |
Pros |
Cons |
|
|
|
||
|
IICS |
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
||
|
|