Entity-based data masking technology allows data security teams to safeguard PII easily, while ensuring relational consistency and contextual integrity.
Top 4 Data Masking Challenges
There are 4 key data masking challenges that are particularly difficult to address for enterprises that have their business data fragmented across dozens of business applications:
-
Ensuring relational consistency
When the same data is scattered among many different source systems (legacy, on-prem, cloud), it may appear differently in different places. For example, the name Nancy Wilson, may appear as Nancy Wilson, N. Wilson, Wilson Nancy, or Wilson N. Your data masking software should be able to mask all these names consistently, across all systems. Similarly, if customer invoices and customer purchases are stored in separate systems, the same masked identifiers must be used across systems, to ensure that the data remains relationally consistent. -
Maintaining dataset contextual integrity
For data anonymization to work properly, an entity’s dataset must retain contextual consistency. For example, if an ISP masks the “state” field in the customer’s mailing address (say, from Oregon to Hawaii), then that person’s home IP address should be masked to correspond to the new mailing address (Hawaii). Also, data that doesn’t match up is suspect, and might tip off potential hackers. -
Achieving dynamic data masking
Dynamic data masking refers to situations when the data needs to be masked in-flight, in near real time. For example, when call center agents can only see the last 4 digits of a credit card number (based on their access rights and privileges), the first 12 digits are masked on the fly. -
Securing a centralized tokenization vault
As a rule, the anonymization of data is irreversible, making it impossible to connect Personally Identifiable Information (PII) to a specific individual. In the case of data tokenization, however, the original sensitive data is stored together with the corresponding tokens (meaningless data) in a centralized token vault. Such a repository, containing everyone’s PII, is a natural target for hackers
Data Masking Technology based on Business Entities
Entity-based data masking technology enables the collection, unification, and anonymization of sensitive data at the granularity of an individual business entity.
In the case of a customer business entity, for example, all relevant PII data from all underlying systems is captured, unified, and masked as a singular dataset (according to a predefined customer data schema) – for each individual customer.
In the case of a “customer” business entity, fragmented data from multiple sources
is synced, processed, compressed, secured, and cached for every single customer.
By masking sensitive data in the context of a business entity, data anonymization can be performed in flight, in near real time. The relational consistency of the masked data (across systems) is easily enforced, as is its contextual integrity.
Data tokenization (a form of pseudonymization) is often used to process payments and conduct online transactions, where personal data has to be securely transmitted and stored – and can be restored to its original form when necessary. If the original data is stored together with the tokens for each business entity in its own “micro-vault”, the risk of breaching a centralized token vault breach is eliminated.
For example, in an insurance company, the QA and software engineering teams might need customer test data – fragmented across multiple systems – for an internal application they’re developing for the claims department. Since customer data inevitably contains PII (Name, DOB, SSN, Role), identifiers must be masked to protect the privacy of the individual customer.
Benefits of a Business Entity Approach
Entity-based data masking tools allow quality, DevOps, and security teams to:
-
Anonymize sensitive data across all structured and unstructured data sources
-
Manage secured micro-vaults, one for every business entity
-
Ensure relational consistency and contextual integrity of the masked data
-
Neutralize PII on the fly, in support of operational use cases
By its very nature, a business entity approach ensures:
- Relational consistency – across all source systems
- Contextual integrity – within the business entity itself
- Dynamic data masking – on demand
- Data security – with zero risk of a mass breach
Implementing the Leading Data Masking Technology
Entity-based data masking technology enables organizations to anonymize data from multiple sources via a business entity data schema.
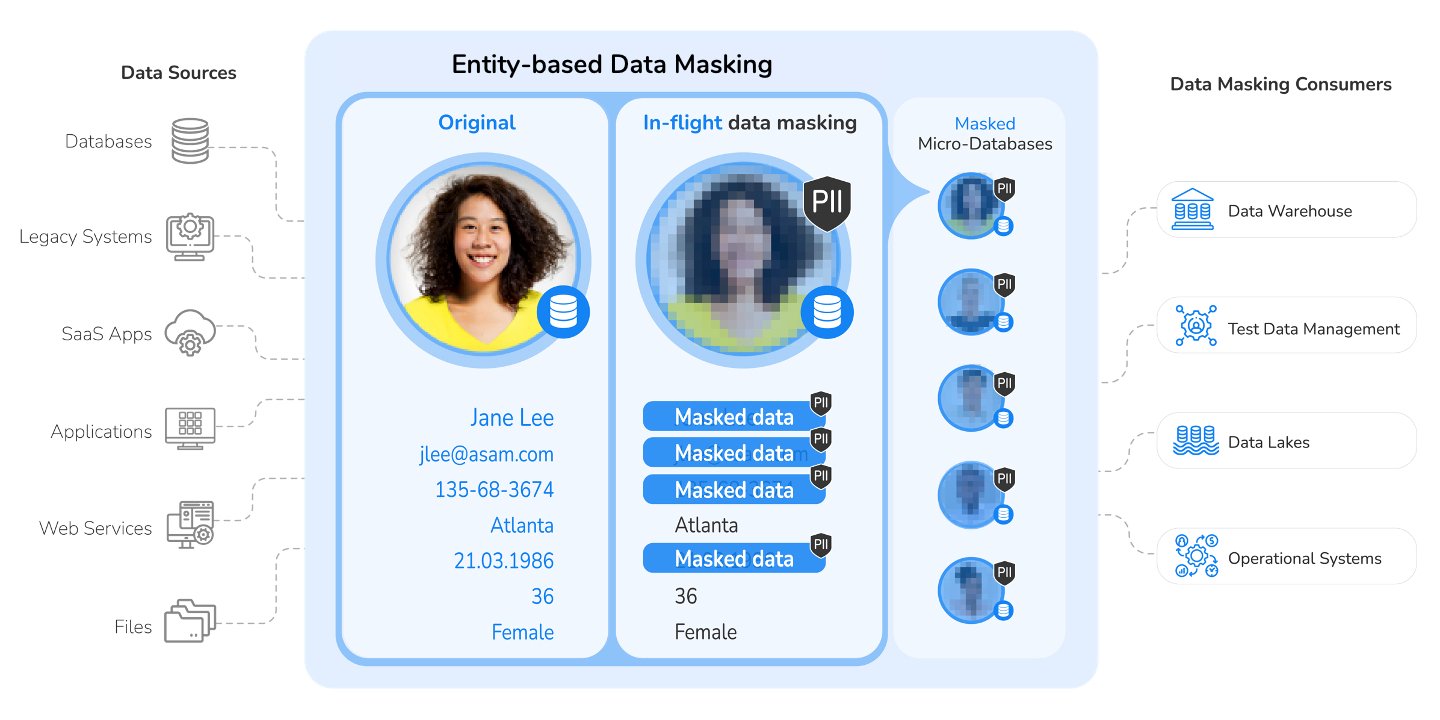
Customer datasets are masked and delivered via individually encrypted Micro-Databases.
Entity-based data anonymization tools let you mask the dataset for each business entity (e.g., a specific customer) in its own, uniquely encrypted Micro-Database™. The dataset for each entity is ingested from the source environment on demand, masked and transformed on the fly, and can be provisioned into any consuming application, quickly and easily.
The entity-based data masking technology makes data masking tools, data tokenization tools, synthetic data generation tools, and test data management tools, significantly safer, faster, and more cost-effective.
Learn more about K2view entity-based data masking tools.