Data anonymization standards are guidelines that ensure that personal or sensitive information cannot be re-identified, to protect an individual’s privacy.
Table of Contents
What are Data Anonymization Standards?
Notable Data Anonymization Standards
Top 10 Challenges Facing Data Anonymization Standards
Leveraging Business Entities to Comply with Data Anonymization Standards
What are Data Anonymization Standards?
Data anonymization standards are sets of guidelines and/or practices that define how to best protect privacy by data de-identification. Such standards ensure that data is consistently de-identified, handled, shared, and stored in a manner that is aligned with best practices, and in compliance with, relevant regulations. Standards are defined either by individual organizations or established regulations.
Data anonymization is important to enterprises because it provides them with the knowledge that the sensitive data they may have collected is safe, reliable, and high-quality. By conforming to data anonymization standards, companies can balance privacy protection and data usability. Such a balance lets them leverage and share data for research, analytics, and innovation, while still maintaining compliance with existing and emerging data privacy legislation – and mitigating the risk of fines, data breaches, brand damage, etc.
Get the Gartner report on data anonymization/masking for FREE.
Notable Data Anonymization Standards
Numerous regional standards relate to data anonymization directly or indirectly. Among the most prominent are:
-
US Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
HIPAA defines standards for de-identification of Protected Health Information (PHI). Under these standards, data anonymization is one method to de-identify PHI, removing identifiers that could link data to a specific individual. Data anonymization allows healthcare organizations to comply with HIPAA requirements, while still using data for research, analysis, and other purposes. -
EU General Data Protection Regulation
GDPR gives data anonymization tools a certain amount of prominence. While it mandates strict protection of Personally Identifiable Information (PII), once data is properly anonymized it no longer falls under the scope of GDPR. This means that organizations that anonymize data correctly are automatically in compliance with GDPR's principles of data minimization, purpose limitation, and accountability. -
ISO/IEC 27559:2022
This fairly recent international standard offers guidelines for data anonymization. Known as a “privacy enhancing data de-identification framework”, this data anonymization standard delineates specific data anonymization techniques and processes that help organizations protect individual privacy while allowing data analysis and sharing. The standard covers principles, methods, and considerations for anonymizing personal data, and also defines specific data masking techniques. -
ISO 29100:2011
This older international standard that provides focuses managing Personally Identifiable Information within organizations. ISO 29100 stresses the need to protect individual privacy by de-identifying PII, and doing so in a way that prevents re-identification of anonymized data. Organizations that adhere to ISO 29100 can be sure they are compliant with numerous privacy laws and regulations, while mitigating the risk of data leakage and preserving data utility. -
UK ISB1523
This UK process standard designed to help organization effectively anonymize their health and social care data. Published by the Information Standards Board for Health and Social Care, part of the UK’s National Health Services (NHS), the standard bridges the gap between the need to protect PII and PHI, and the obligation to provide transparency and release information under the UK’s Freedom of Information Act. This standard draws a clear line between identifying and non-identifying data, and offers guidelines for the anonymization of data in general.
Top 10 Challenges Facing Data Anonymization Standards
The 10 most pressing issues facing organizations vis-à-vis data anonymization standards are:
-
De-identification efficacy
Enterprises are challenged to ensure that anonymization techniques are used effectively – removing or altering identifying information while minimizing the risk of re-identification. -
Quality and utility of data
It’s challenging for companies to strike the right balance between preserving data utility for software testing, analysis, or research purposes, and effectively protecting Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and other sensitive data via data anonymization. -
Maintaining context
When anonymizing data, it’s crucial for firms to preserve referential integrity to maintain internal business logic and accurate analysis. -
Technology and security
Data governance teams must constantly coordinate their anonymization practices with security teams measures to keep pace with emerging technologies and threats. -
Data protection
Privacy laws and data anonymization standards are constantly evolving. Organizations need to maintain constant vigilance to ensure they’re meeting both current and future requirements. -
Data sharing
Sharing data across international borders is becoming legally and technically complex due to multiple data privacy laws that span different jurisdictions. -
Cross-company sharing and communication
Similarly, cooperating 3rd-party companies must ensure the consistency and integration of data anonymization standards to facilitate interoperability. -
Ethical considerations
Organizations need to make sure that ethical considerations – like ensuring fairness, avoiding bias, and safeguarding against potential discrimination – are effectively incorporated in their data anonymization solution. -
Data governance
To both ensure and demonstrate responsible data handling throughout the data anonymization process, enterprises must create and apply clear data governance frameworks and accountability mechanisms. -
Awareness and education
To foster a better understanding of both the importance and the challenges of data anonymization, organizations need to promote awareness and education about data masking best practices with the organization itself, as well as between different domains, data custodians and data users.
Leveraging Business Entities to Comply with Data Anonymization Standards
Data anonymization standards offer guidelines to protect privacy while enabling data usability. Yet challenges remain. Efficacy, data quality, technology updates, regulations, cross-border sharing, and ethical considerations – all require ingenuity and persistence on the part of companies and governing bodies.
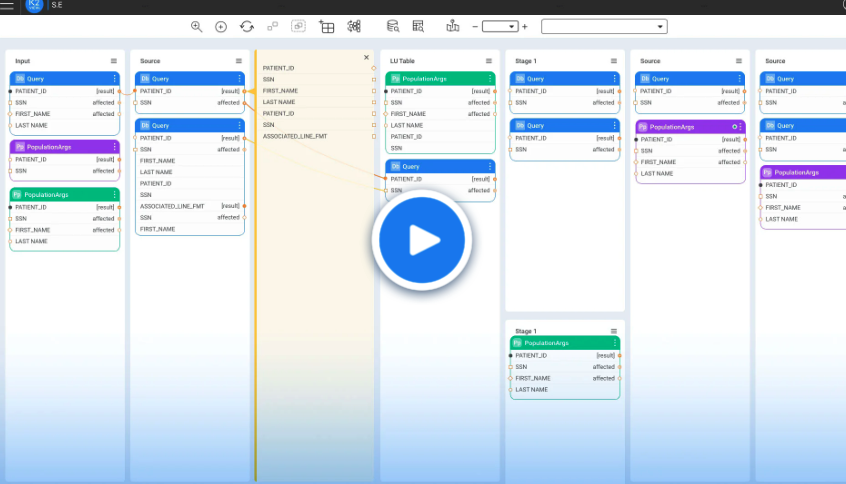
With entity-based data masking technology, data teams can anonymize data more quickly and efficiently. It integrates and organizes fragmented data from multiple source systems according to data schemas – where each schema corresponds to a business entity (such as a customer, vendor, or order).
This context-preserving approach to meeting data anonymization standards enhances productivity, ensures regulatory compliance, and safeguards customer privacy.
Learn more about entity-based data anonymization tools.